50 mL of 0.1 M solution of sodium acetate and 50 mL of 0.01 M acetic acid are mixed. The pKa of acetic acid is 4.76. The pH of the buffer solution is:

You have 250mL of a 0.56M solution of sodium acetate. How many mL of 0.50M acetic acid should be added to make a buffer of pH 4.40? | Homework.Study.com

SOLVED: 16. Which of the following could be added to a solution of sodium acetate to produce a buffer? A) acetic acid only B) acetic acid or hydrochloric acid C) hydrochloric acid

Sodium Acetate(CH3COONa) - Structure, Properties, Preparations, Uses, Important questions, FAQs of sodium acetate.
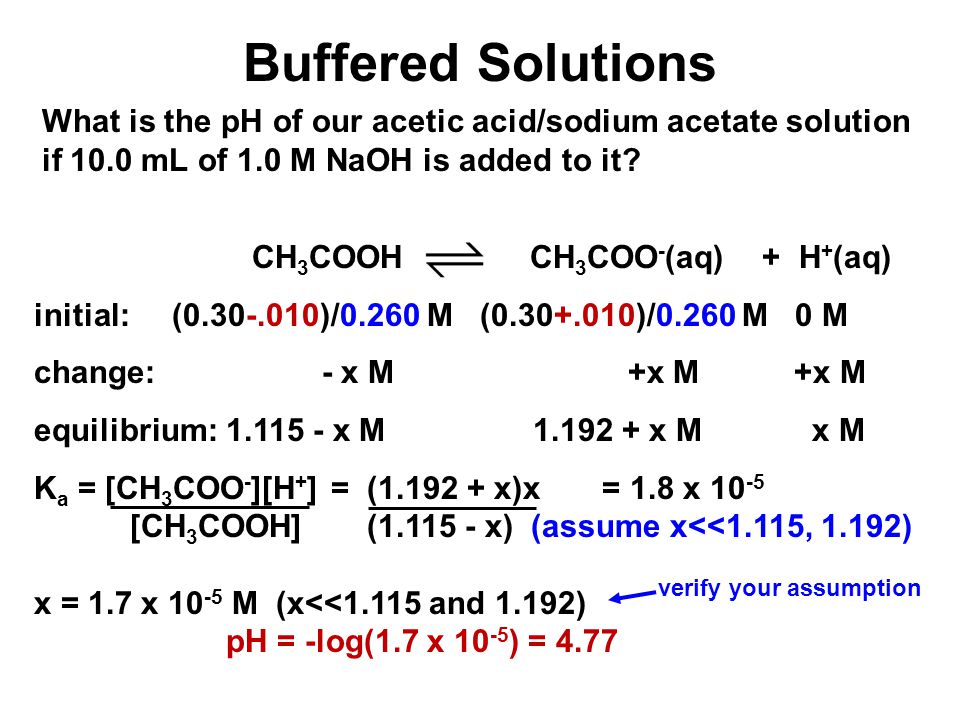
Prove the buffer action of acetic acid and sodium acetate by the addition of 0.01 mol of solid sodium hydroxide. - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community

1 Chapter 10 Acids and Bases 10.9 Buffers. 2 When an acid or base is added to water, the pH changes drastically. A buffer solution resists a change in. - ppt download

If sodium acetate is a weak acid and does not readily dissociate in water or completely and a strong electrolyte is defined as the oppposite how come the answer is B and

SOLVED: Acetic acid (CH3COOH, 𝐾a=1.80×10−5) is a weak acid, so the salt sodium acetate (CH3COONa) acts as a weak base. Calculate the pH of a 0.809 M solution of sodium acetate. pH=

What is the pH of buffer solution containing 0.17 M acetic acid and 0.36 M sodium acetate? - YouTube

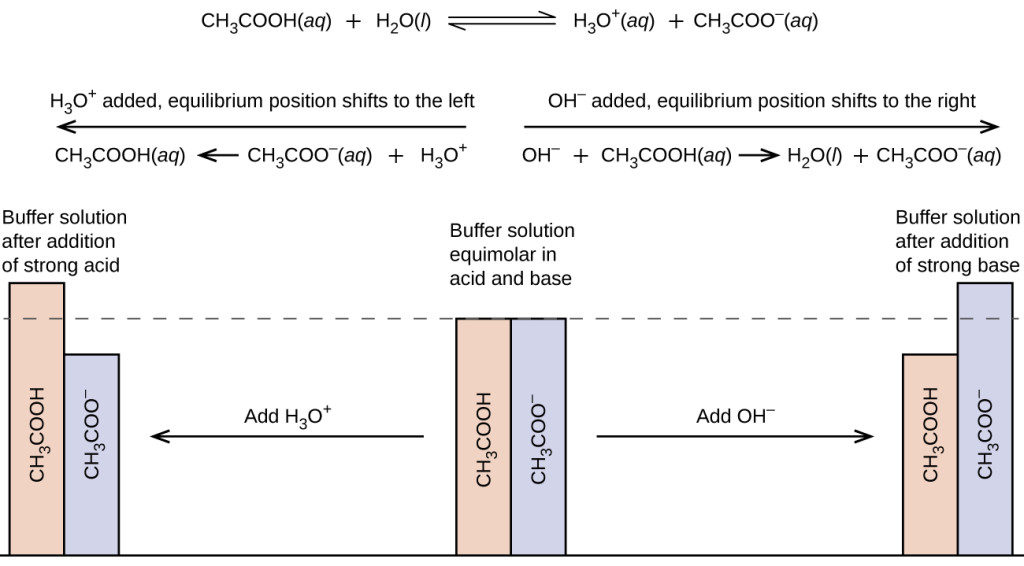
SCH 4 U 1. What are buffers? Buffers are mixtures of conjugate acid- base pairs that allow a solution to resist changes in pH when acids and/or bases. - ppt download
Why does the solution of sodium acetate give more concentration of Hydroxide ion? Shouldn't the number of Hydroxide ion and hydrogen ion be equal? - Quora